December 15, 2013 - 7:58 pm by Joss Whittle
C/C++ Graphics PhD University
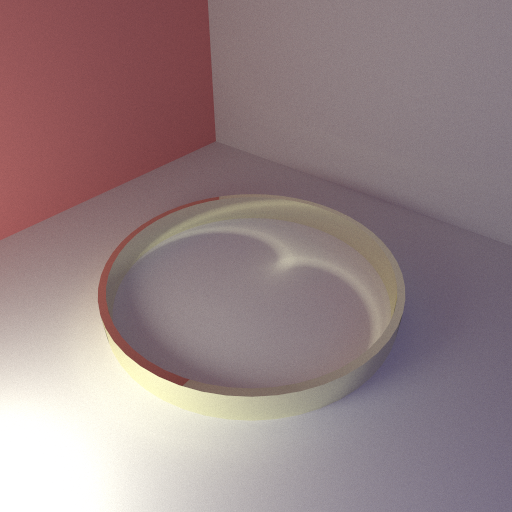
Thought it was about time to test some caustics on the renderer. Lately I’ve been both fascinated and frustrated by the strange forms and shapes that occur when light refracts and reflects off of lit surfaces. A great example of this is a metallic ring laying on a diffuse surface. Light bouncing onto the inside edge of the ring will be focused downwards onto the floor plane in a curved m shape causing a bright spot.
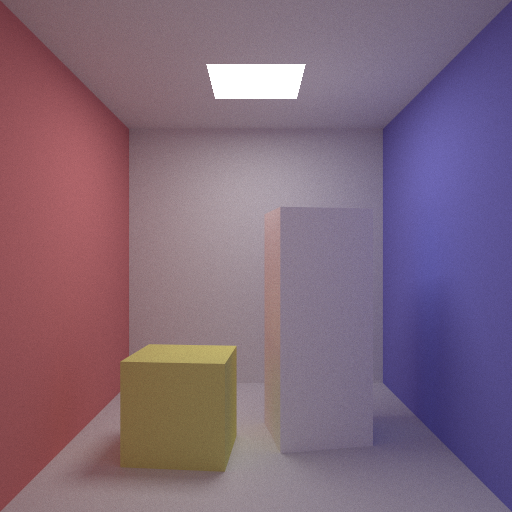
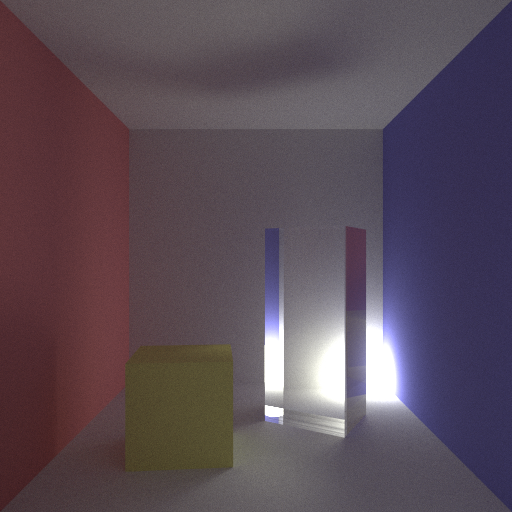
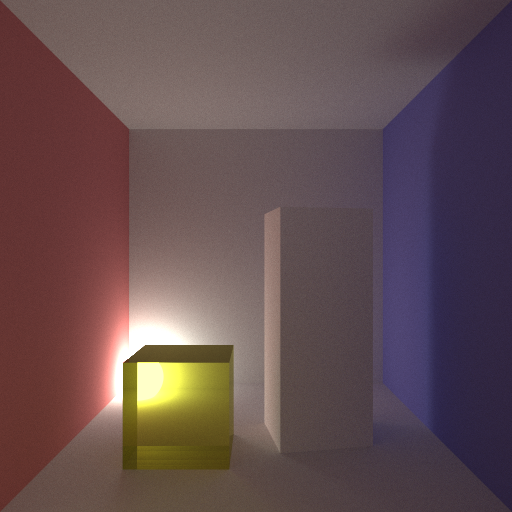
I’ve also been playing around with scenes that employ more indirect lighting. By this I mean scenes where the light source(s) are mostly if not entirely occluded from direct view by the camera. To this effect I set a standard cornell box scene with a yellow cube and a white oblong inspired by Cohen & Greenberg,and placed an occluded light sphere in the back-bottom corner of the room. I then toggled which of the two hemicubes were made of glass to see how the light would refract through them.
Tags
Global Illumination, Monte Carlo Integration, Path Tracing
December 13, 2013 - 12:39 am by Joss Whittle
C/C++ Graphics PhD University
Tags
Global Illumination, Monte Carlo Integration, Path Tracing
December 9, 2013 - 10:33 am by Joss Whittle
C/C++ Graphics PhD University
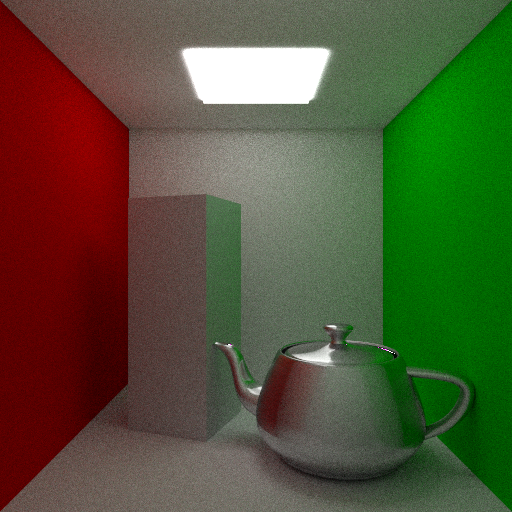
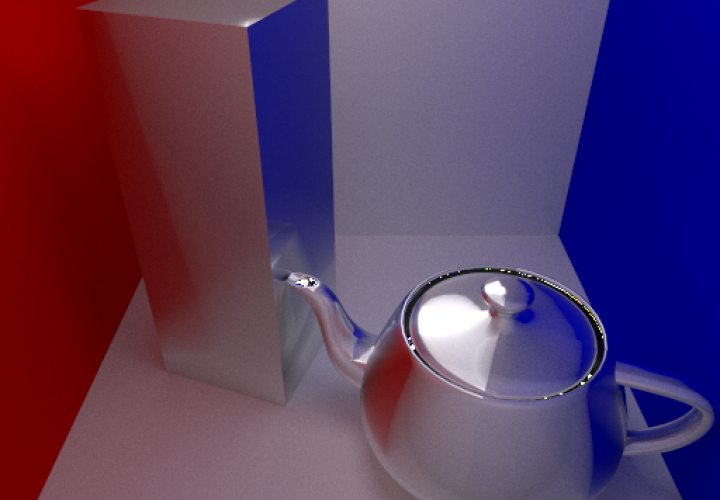
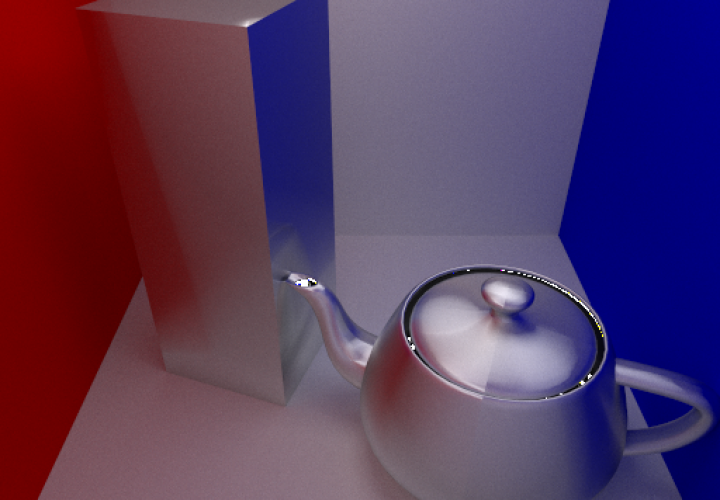
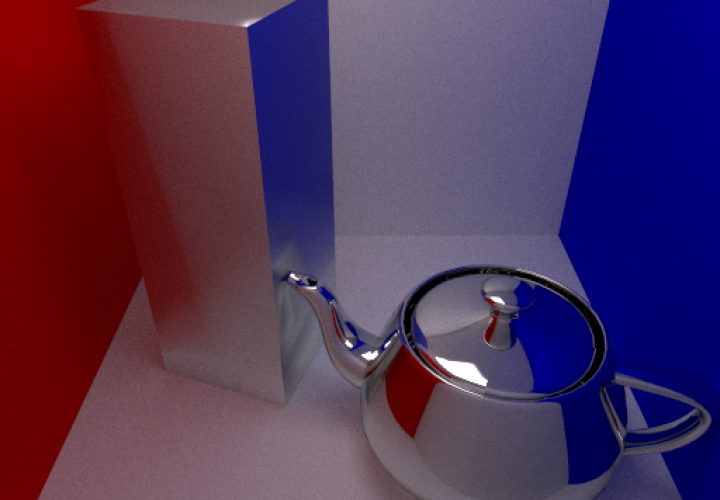
I thought I’d make some high quality comparison shots of some of the shaders I’ve been working on. Above you can see a side by side comparison of a perfect mirror BRDF and a Phong based BRDF with exponents of one million and ten for the centre and right images respectively.
While the Phong-like BRDF does give nice glossy reflections at a relatively small cost it does not model a physically accurate shader. I’m currently looking into implementing a Cook–Torrance model shader which while being more time consuming to compute gives nice results which are based off of physical phenomena. The Cook–Torrance shader also has the inherent ability to model microfacets within the surface of objects which is a big plus.
Because the Phong BRDF is not physically accurate I needed to find a PDF that would look correct in the renderings. The Mirror BRDF for instance has a PDF = 1 and the Diffuse BRDF has a PDF = 2 * (normal . newDirection). After some experimenting from reading a paper that claimed the Phong marginal pdf was cos(theta)^e which I understood (possibly incorrectly as it did not work) to mean PDF = (normal . newDirection)^e I found (gave up) that the Diffuse BRDF in fact worked reasonably well for the Phong model.
Edit I have found a better paper with what looks like a good Phong model. They even give a run down of using their model in a Monte Carlo style simulation with a marginal PDF. I might try implementing this before I move onto Cook-Torrance.
Tags
Global Illumination, Monte Carlo Integration, Path Tracing
December 6, 2013 - 2:20 pm by Joss Whittle
C/C++ Graphics PhD University
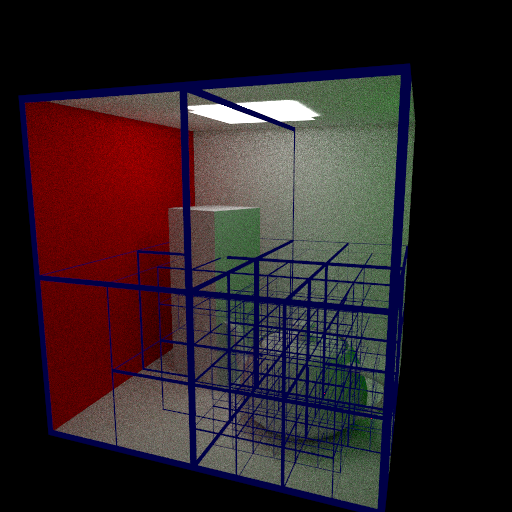
Previously I’ve debugged my KD-trees only by looking at archaic console printouts where at best each descending node in the structure is tabbed a couple of spaces further in from it’s parent.
However, seeing as I’m currently building a new renderer it seemed apt to build in a method for visualizing the generated trees. This was pretty simple to add in, if a preprocessor flag __AABB_EDGE__ is defined at compile time then during tree traversal additional code will run which does a simple UV coordinate calculation for the Axis Aligned-Bounding Box; if the UV is close enough to the edge of the box then the current pixel is abandoned and set to plain blue. The result is quite interesting to view and because of the power of the C++ preprocessor when it is disabled it effectively doesn’t exist in the compiled executable, meaning it has no effect on performance.
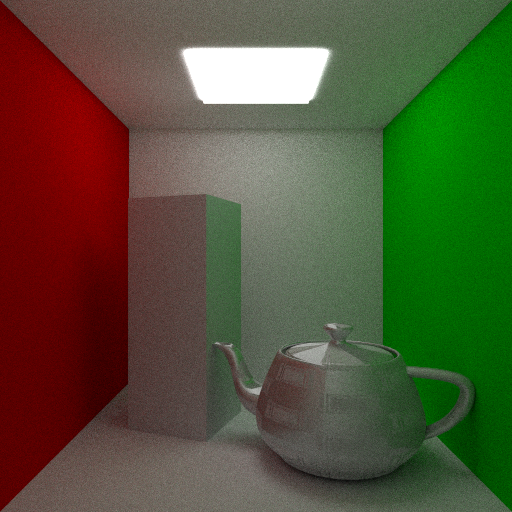
I have also been playing with specular and normal mapping. It was trivial to add due to the design of the shader class this time. In the case of specular mapping the max value of each RGB tuple is taken as the value for the map on the [0,1] range; this is then used to linearly scale the specular exponent of the shader which is used to calculate the glossy reflection for surfaces with an exponent > 0. Below a checker-board texture was used to scale a specular exponent of 128 into regions of 0 and 128 over the surface of the teapot.
Tags
Global Illumination, Monte Carlo Integration, Path Tracing
December 3, 2013 - 9:43 pm by Joss Whittle
C/C++ Graphics PhD
Today has been a pretty good day, both for me and for my work. For the last couple of weeks I’ve been working from home because all I am doing lately is background reading and coding my new renderer. At first it was nice to know that my workspace was only a commando roll (or a fall) out of bed away from me; but after 3 weeks it just got to be a bit much. Don’t take this to mean I didn’t leave the house for three weeks, I did, but working long hours from the comfort of my room did dramatically take its toll on me.
But enough about me going mad in the house! Today I came into the office (which I think I’ll start doing a lot more often) and have made great progress on my new C++ render!
Tags
Concurrency, Global Illumination, Monte Carlo Integration, Path Tracing, Ray Tracing